Virtualization

Virtualization
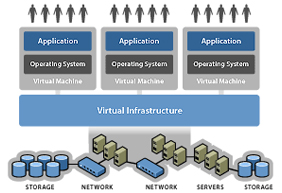
virtual(rather than actual) version of something, such as an operating system, a server, a storage device or network resources. Operating system virtualization is the use of software to allow a piece of hardware to run multiple operating system images at the same time. The technology got its start on mainframes decades ago, allowing administrators to avoid wasting expensive processing power. The idea is that virtualization disguises the true complexity of the network by separating it into manageable parts, much like your partitioned hard drive makes it easier to manage your files.
Server virtualization is the masking of server resources (including the number and identity of individual physical servers, processors, and operating systems) from server users.
Network virtualization is a method of combining the available resources in a network by splitting up the available bandwidth into channels, each of which is independent from the others, and each of which can be assigned (or reassigned) to a particular server or device in real time.
Storage virtualization is the pooling of physical storage from multiple network storage devices into what appears to be a single storage device that is managed from a central console. Storage virtualization is commonly used in storage area networks (SANs).